Epoxy is a thermosetting adhesive glue made of resin, which is used as a hardener. Epoxy is also used to adhere different surfaces together, which can withstand extreme stress and weather conditions. However, adhesive means sticking, whether it is on the surface of the object. Read More…
Master Bond formulates high quality adhesive systems to help engineers meet specific requirements for their bonding, sealing, coating and encapsulation applications. The product line consists of epoxies, silicones, UV curable and LED curable systems that feature outstanding performance properties.

We hold North American manufacturing together with our adhesives! We have presences in Seattle, Portland, Spokane, Houston, Dallas, Tulsa, Chicago and many others so that we will be where you need us, always! Our motto states that “We strive for insanely happy customers,” and that’s exactly what the kind of commitment to excellence that we will bring to you. For more information on what we...
We hold North American manufacturing together with our adhesives! We have presences in Seattle, Portland, Spokane, Houston, Dallas, Tulsa, Chicago and many others so that we will be where you need us, always! Our motto states that “We strive for insanely happy customers,” and that’s exactly what the kind of commitment to excellence that we will bring to you. For more information on what we...
More Epoxy Adhesive Manufacturers
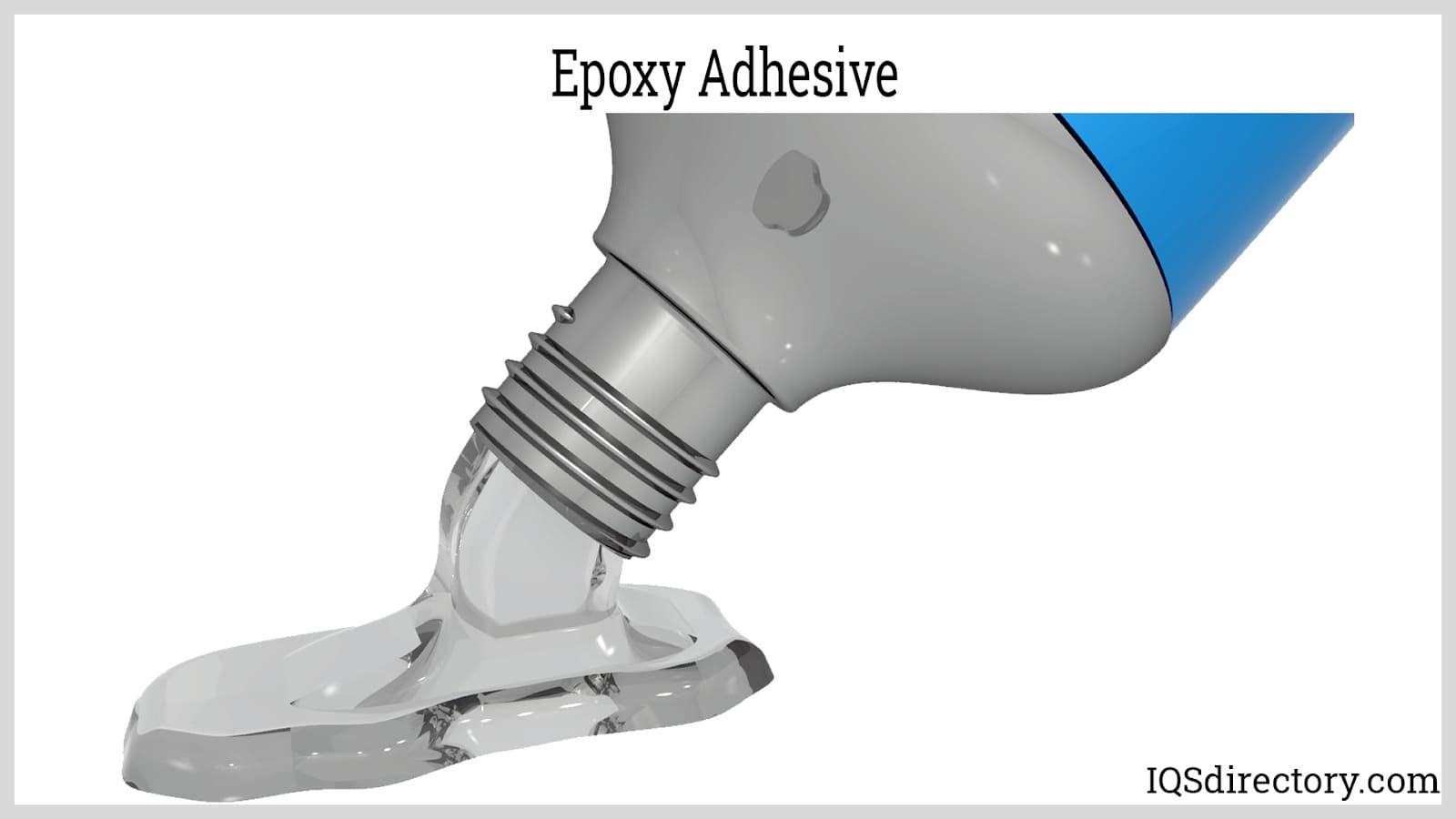
Epoxy adhesive is a versatile, high-performance bonding agent widely used across a range of industries—such as manufacturing, construction, electronics, automotive, marine, and aerospace—thanks to its superior strength, durability, and chemical resistance. As a specialized type of industrial glue, epoxy adhesives are formulated from various epoxy resins, each offering unique properties tailored to different application requirements. For example, heat-resistant epoxy adhesives are ideal where elevated temperature stability is essential, while flexible epoxy adhesives are suited for applications needing vibration absorption or impact resistance.

What Is Epoxy Adhesive? Understanding Epoxy Resin-Based Glues
Epoxy adhesive, often referred to as epoxy glue or structural adhesive, is a two-part system consisting of a resin and a hardener (also called a curing agent). When these components are mixed, a chemical reaction called polymerization occurs, resulting in a strong, rigid thermoset plastic. This reaction can be tailored with additives and modifiers to enhance specific properties like toughness, flexibility, thermal conductivity, or chemical resistance, making epoxy adhesives a preferred choice for demanding industrial, commercial, and even household applications.
How Are Epoxy Adhesives Made? Composition and Formulation
Manufacturing epoxy adhesives begins by polymerizing two core components: the epoxy resin and the hardener. The epoxy resin is typically synthesized from the reaction of epichlorohydrin with bisphenol-A (BPA) or bisphenol-F, resulting in a thermosetting polymer. The hardener, commonly an amine-based compound, initiates the curing process when mixed with the resin. To achieve specific performance characteristics, manufacturers may incorporate additives such as:
- Fillers – Increase bulk, improve gap-filling, and alter mechanical properties.
- Tougheners and plasticizers – Enhance impact resistance and flexibility.
- Silane coupling agents – Improve adhesion to different substrates.
- Defoamers – Prevent air entrapment during mixing and application.
- Colorants – Aid in process identification and aesthetics.
The curing process of epoxy adhesive is exothermic, meaning it releases heat as the resin and hardener react. By adjusting the temperature, resin selection, and hardener chemistry, engineers can fine-tune properties such as mechanical strength, thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation. These variables allow for the development of custom epoxy formulations for virtually any industrial or commercial bonding requirement.
Classes of Epoxy Adhesives: One-Component vs. Two-Component Systems
Epoxy adhesives are typically categorized as either one-component (1K) or two-component (2K) systems, with each class offering distinct advantages and best-use scenarios:
Two-Component Epoxy Adhesive
The two-component epoxy adhesive system is the most common and versatile type, requiring users to mix resin and hardener in a precise ratio before application. This initiates the curing reaction, resulting in an extremely strong, durable bond. The 2K system offers the flexibility to adjust working time (pot life), open time, and cure speed by altering the ratio or selecting specific hardeners. For faster processing or to accelerate curing, heat or UV radiation can be applied. 2K epoxy adhesives are widely used to bond a range of substrates, including wood, metal, plastics, ceramics, composites, and rubber, making them ideal for structural bonding, repair, and assembly applications.

- Strengths: Highest mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and reliability.
- Typical uses: Industrial assembly, automotive repair, composite fabrication, heavy-duty construction, and high-performance applications.
- User tip: Looking for maximum bond strength for critical assemblies? Explore high-strength epoxy adhesives for metal-to-metal or composite bonding.
Single-Component Epoxy Adhesive
Single-component (1K) epoxy adhesives simplify the application process, as they come premixed and ready to use—no mixing required. These adhesives often have a paste or gel consistency, ideal for gap filling or surface leveling, especially between metal components. Most 1K epoxies require elevated temperatures (typically 120°C to 180°C) to cure, making them suitable for production processes with heat-curing ovens. Their ease of use and controlled application make them popular for electronics assembly, automotive manufacturing, and certain construction scenarios.

- Strengths: Convenience, precise application, and consistent results.
- Limitations: Typically lower ultimate strength than 2K systems and may require heat for curing.
- Common uses: Electronics potting, surface mounting, home repair, and bond-line filling.
- How do you choose: Need a fast, no-mix solution for electronics or small repairs? Consider single-part epoxy adhesives for ease of use and reliable performance.
Types of Epoxy Adhesives: Resin Variants and Specialty Formulations
The broad family of epoxy adhesives encompasses several resin chemistries and specialty blends, each engineered for a unique set of performance demands. The most common types include:
DGEBA Epoxy Resin (Diglycidyl Ether of Bisphenol A)
- DGEBA epoxy is the earliest and most widely used type, prized for its versatility and compatibility with numerous catalysts and curing agents.
- Available as low-molecular-weight liquids, solids, semi-solids, and brominated resins (for flame-retardant applications).
- Key properties: Excellent mechanical strength, good chemical resistance, and customizable cure profiles.
- Typical uses: Structural bonding, composite lamination, coatings, and flame-retardant applications in electronics and construction.
Waterborne Epoxy Adhesives
- While most epoxies are hydrophobic and do not dissolve in water, waterborne epoxy adhesives are formulated as emulsions or dispersions for easier application and lower VOC emissions.
- The mechanical and chemical stability depends on the surfactants and manufacturing processes used.
- Popular in eco-friendly applications, concrete coatings, and flooring adhesives.
- Interested in sustainable bonding solutions? Discover water-based epoxy adhesives for low-odor, environmentally responsible projects.
Epoxy Acrylate Resins
- Blended from vinyl ester resins or specialized radiation-curing epoxy acrylates, these adhesives cure rapidly—often at room temperature or via UV exposure.
- Benefits include lower viscosity, increased flexibility, and improved wetting for difficult surfaces.
- Ideal for fast-setting industrial adhesives, dental and medical device assembly, and rapid prototyping.
- Looking for a quick-cure adhesive? Epoxy acrylate resins offer exceptionally fast handling times and adaptable cure mechanisms.

Flexible Epoxy Resin Glues
- Formulated with elastomeric modifiers to increase flexibility and impact resistance, reducing the inherent brittleness of standard epoxy.
- Used for laminating safety glass, vibration and sound damping, and encapsulating sensitive electrical components.
- Offers a balance between structural strength and resilience, making them suitable for dynamic assemblies and substrates prone to movement.
- Flexible epoxy adhesives are especially valuable in automotive, marine, and electronics sectors.
Epoxy Novolac Adhesives
- Produced from phenolic novolac resins, these adhesives provide outstanding chemical and thermal resistance.
- Preferred in harsh environments, such as chemical processing plants, oil & gas, and high-temperature assemblies.
- Their high viscosity can challenge manufacturing and application, but their performance in aggressive conditions is unmatched.
- Epoxy novolac adhesives are the go-to option where both strength and chemical durability are mission-critical.
UV Hybrid Epoxy Adhesives
- Combine UV-curable acrylates with thermally curable epoxies for dual-cure flexibility.
- Fixture times are dramatically reduced (from minutes to seconds) with UV exposure, while the epoxy component ensures long-term strength and thermal stability.
- Used in electronics, medical device assembly, and precision manufacturing where speed and reliability are both essential.
- Question: Need a fast, reliable bond in automated assembly? UV hybrid epoxies may be the solution for enhanced production efficiency.
Key Applications of Epoxy Adhesives: Where and Why Are They Used?
Thanks to their robust performance and adaptability, epoxy adhesives serve critical roles in many sectors. Common applications include:
- Chemical resistance: Used in pipelines, storage tanks, and chemical processing equipment where exposure to acids, solvents, and corrosive agents is routine.
- Automotive manufacturing: Dampen vibrations and noise, bond structural panels, and enable lightweight composite assemblies.
- Aerospace & aviation: Bind helicopter blades, structural components, and honeycomb panels, meeting stringent strength-to-weight and fatigue requirements.
- Marine environments: Provide saltwater resistance for boat building, ship repair, and underwater construction.
- Construction industry: Used for anchoring bolts, repairing concrete, waterproofing, and exterior weather-resistant applications.
- Electronics: Potting and encapsulating sensitive circuits, providing insulation, vibration damping, and moisture protection.
- Renewable energy: Bonding wind turbine blades and assembling photovoltaic panels.
- DIY and household repairs: Epoxy glues are popular for fixing furniture, ceramics, jewelry, and more due to their strength and versatility.
Want to explore more? Try searching:
“Best epoxy adhesive for metal” | “Epoxy glue for plastics” | “Marine-grade epoxy suppliers” | “High-temperature resistant epoxy manufacturers” | “Epoxy for electronics potting”
Benefits of Epoxy Adhesives: Why Choose Epoxy Over Other Bonding Solutions?
- Exceptional bond strength: Outperforms many other adhesive types, providing structural-grade adhesion for demanding assemblies.
- Versatile substrate compatibility: Bonds metals, plastics, ceramics, composites, glass, wood, and more.
- Chemical and environmental resistance: Resists degradation from water, oils, chemicals, and UV exposure.
- Thermal and electrical insulation: Ideal for electronics and high-temperature applications.
- Customizable formulations: Available in a range of viscosities, cure times, colors, and flexibilities for tailored solutions.
- Gap-filling capabilities: Fills irregular surfaces and voids for robust joints.
- Long-term durability: Maintains bond integrity under dynamic loads, vibration, and harsh conditions.
Epoxy adhesives are the preferred choice for manufacturers, engineers, contractors, and DIY enthusiasts seeking reliable, long-lasting bonds in critical applications. The ability to engineer custom solutions makes epoxy adhesives a cornerstone of modern assembly, repair, and manufacturing processes.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Epoxy Adhesive
Choosing the right epoxy adhesive is crucial for ensuring performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Key decision factors include:
- Substrate compatibility: Is the adhesive formulated for the specific materials you need to bond (e.g., metal, plastic, composite)?
- Strength requirements: What are the load-bearing and durability needs of your application?
- Cure time and processing: Do you have time constraints, or do you need a fast-setting or extended working time adhesive?
- Temperature and environmental resistance: Will the bond be exposed to high heat, moisture, chemicals, or UV radiation?
- Application method: Are you dispensing by hand, automated equipment, or using pre-mixed cartridges?
- Regulatory and safety considerations: Does your process require low-VOC adhesives, flame retardance, or food-safe certification?
- Cost and efficiency: What is your budget, and how does adhesive performance impact overall process economics?
Confused about which epoxy to choose? Use targeted searches like:
“Epoxy adhesive for plastic to metal” | “Food-safe epoxy manufacturer” | “Fast-curing epoxy for assembly lines” | “Low-temperature cure epoxy” to narrow your options based on your requirements.
How to Apply Epoxy Adhesive: Best Practices for Maximum Performance
Proper application is key to achieving optimal bond strength and durability. Follow these steps for best results:
- Surface Preparation: Clean and degrease surfaces. Abrade glossy or smooth surfaces to improve mechanical adhesion.
- Mixing: For 2K systems, mix resin and hardener thoroughly in the recommended ratio.
- Application: Apply adhesive evenly to both surfaces, ensuring complete coverage. For gap-filling, use a spatula or injection method.
- Assembly: Join components and clamp if required. Maintain alignment during the cure process.
- Curing: Allow sufficient time for the adhesive to reach full strength. Use heat or UV if specified for accelerated curing.
- Finishing: Remove excess adhesive and inspect the bond for completeness and quality.
For automated or industrial-scale processes, consider using dispensers, static mixers, and curing ovens to streamline application and improve consistency.
Choosing the Correct Epoxy Adhesives Manufacturer
To ensure the most successful outcome when purchasing epoxy adhesives from a reputable supplier, it’s crucial to evaluate multiple manufacturers based on technical expertise, product range, and customer support. Here’s how to make an informed decision:
- Compare suppliers: Review at least four epoxy adhesive companies to assess their experience, product offerings, and service quality.
- Company profiles: Each manufacturer’s business profile page details specialized capabilities, certifications (ISO, REACH, RoHS), and unique value propositions.
- Direct communication: Use integrated contact forms to request technical data, samples, or a customized quote for your specific application.
- Website previews: Explore company websites via our proprietary previewer to understand expertise in automotive adhesives, marine epoxies, construction bonding agents, or electronics-grade formulations.
- Request for Quote (RFQ): Send a single message to multiple manufacturers for competitive pricing and tailored recommendations.
Ready to source epoxy adhesives? Search for:
“Epoxy adhesive suppliers near me” | “Custom epoxy formulation manufacturer” | “Bulk epoxy resin distributor” | “Specialty adhesive companies USA”
Frequently Asked Questions About Epoxy Adhesives
How do I choose between 1K and 2K epoxy adhesives?
Consider cure speed, application method, and required bond strength. 1K systems offer easy handling but typically require heat, while 2K systems deliver higher strength and versatility with manual mixing.
Can epoxy adhesives bond plastics and metals?
Yes, but substrate preparation and adhesive selection are key. Certain epoxies are engineered for plastic-to-metal bonding, ensuring excellent adhesion and durability.
What is the shelf life of epoxy adhesives?
Properly stored, most epoxy resins and hardeners last 1-2 years. Always check manufacturer specifications and store in cool, dry environments.
Are there food-safe or medical-grade epoxy adhesives?
Yes, specialized formulations are available for food processing, potable water, and medical device assembly. Always confirm certifications with the manufacturer.
How can I remove cured epoxy adhesive?
Mechanical removal (scraping, sanding) is most effective. Chemical strippers may be used for some formulations—consult product documentation for safe removal techniques.
Conclusion: The Value of Epoxy Adhesives in Modern Industry
Epoxy adhesives have revolutionized modern manufacturing, construction, and repair by providing unmatched strength, reliability, and adaptability. Whether you need a structural adhesive for heavy-duty assembly, a quick-curing glue for rapid prototyping, or a high-performance solution for harsh environments, the wide array of epoxy adhesive chemistries ensures there’s an ideal product for every application. By understanding the unique benefits, types, and application methods, you can select the right epoxy adhesive to maximize productivity, safety, and end-product quality.
Ready to take the next step? Browse our directory of epoxy adhesive manufacturers to request technical data, compare formulations, and connect with industry experts for your next project.




 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services