Adhesives are materials that join two surfaces together, typically by creating a bond. The use of adhesives dates back to prehistoric times when early humans used natural adhesives like tree resin and animal hide glue to make tools and weapons. Over time, adhesives became more sophisticated, and new materials and formulations were developed. For example, the ancient Egyptians used animal glue and beeswax to bind papyrus scrolls, while the Romans used a mixture of lime and volcanic ash to make cement. Read More…
Master Bond formulates high quality adhesive systems to help engineers meet specific requirements for their bonding, sealing, coating and encapsulation applications. The product line consists of epoxies, silicones, UV curable and LED curable systems that feature outstanding performance properties.

We hold North American manufacturing together with our adhesives! We have presences in Seattle, Portland, Spokane, Houston, Dallas, Tulsa, Chicago and many others so that we will be where you need us, always! Our motto states that “We strive for insanely happy customers,” and that’s exactly what the kind of commitment to excellence that we will bring to you. For more information on what we...
At Parson Adhesives, Inc., we specialize in providing comprehensive adhesive solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clientele. With years of experience and expertise in the adhesive industry, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader in adhesive manufacturing, renowned for our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction.

More Adhesive Manufacturers
The evolution of adhesives during the 20th century, particularly with the development of synthetic polymers, transformed the way materials are joined in countless industries. Modern adhesives such as epoxy, cyanoacrylate (superglue), and polyurethane have become foundational not only in daily life—supporting everything from children’s art projects to home repairs—but also in high-stakes sectors like aerospace engineering and medical device manufacturing. As adhesive technologies continue to advance, they are unlocking new possibilities for product design, assembly, and construction.
Types of Adhesives: Exploring Formulations and Industry Use Cases
Adhesives are available in a wide range of formulations, each engineered to satisfy specific bonding challenges. Understanding the different types of adhesives is crucial for manufacturers, engineers, and end-users looking to select the optimal adhesive product for their application. Below, we detail some of the most prominent adhesive types, their properties, and common industry uses:
-
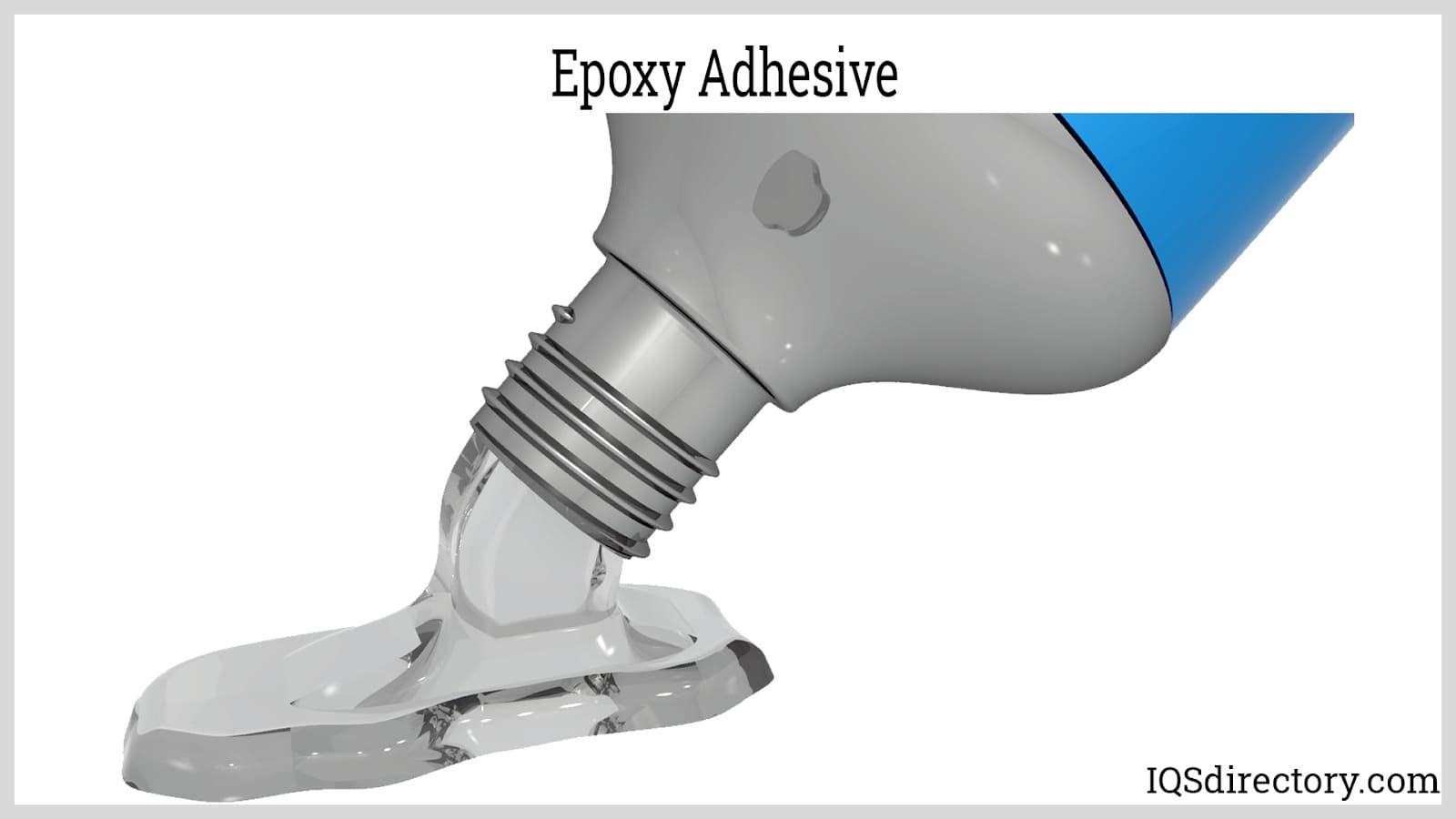
Epoxy Adhesives: Composed of a resin and a hardener, epoxy adhesives are renowned for their exceptional strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. These two-component adhesives are widely used in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, electronics, and marine applications due to their ability to create robust, long-lasting bonds.
- Common use cases: Bonding structural components, composite materials, automotive panels, wind turbine blades, and electronic assemblies.
- Key benefits: High mechanical strength, resistance to water and solvents, excellent gap-filling properties.
-
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Superglue): These instant adhesives are fast-setting and form durable bonds across a variety of surfaces, including plastics, metals, ceramic, and rubber. Cyanoacrylates are a staple in woodworking, electronics assembly, medical device manufacturing, and emergency wound closure.
- Common use cases: Repairing small parts, assembling electronics, closing surgical incisions, crafting and hobby projects.
- Key benefits: Rapid curing at room temperature, strong adhesion to a wide range of substrates, minimal clamping required.
-
Polyurethane Adhesives: Valued for their flexibility, impact resistance, and moisture/chemical resistance, polyurethane adhesives are heavily used in construction, automotive assembly, furniture production, and footwear manufacturing.
- Common use cases: Sealing and bonding in construction, laminating fabrics, automotive glass installation, shoe sole attachment.
- Key benefits: Excellent flexibility, good adhesion to dissimilar materials, ability to withstand dynamic stresses.
-
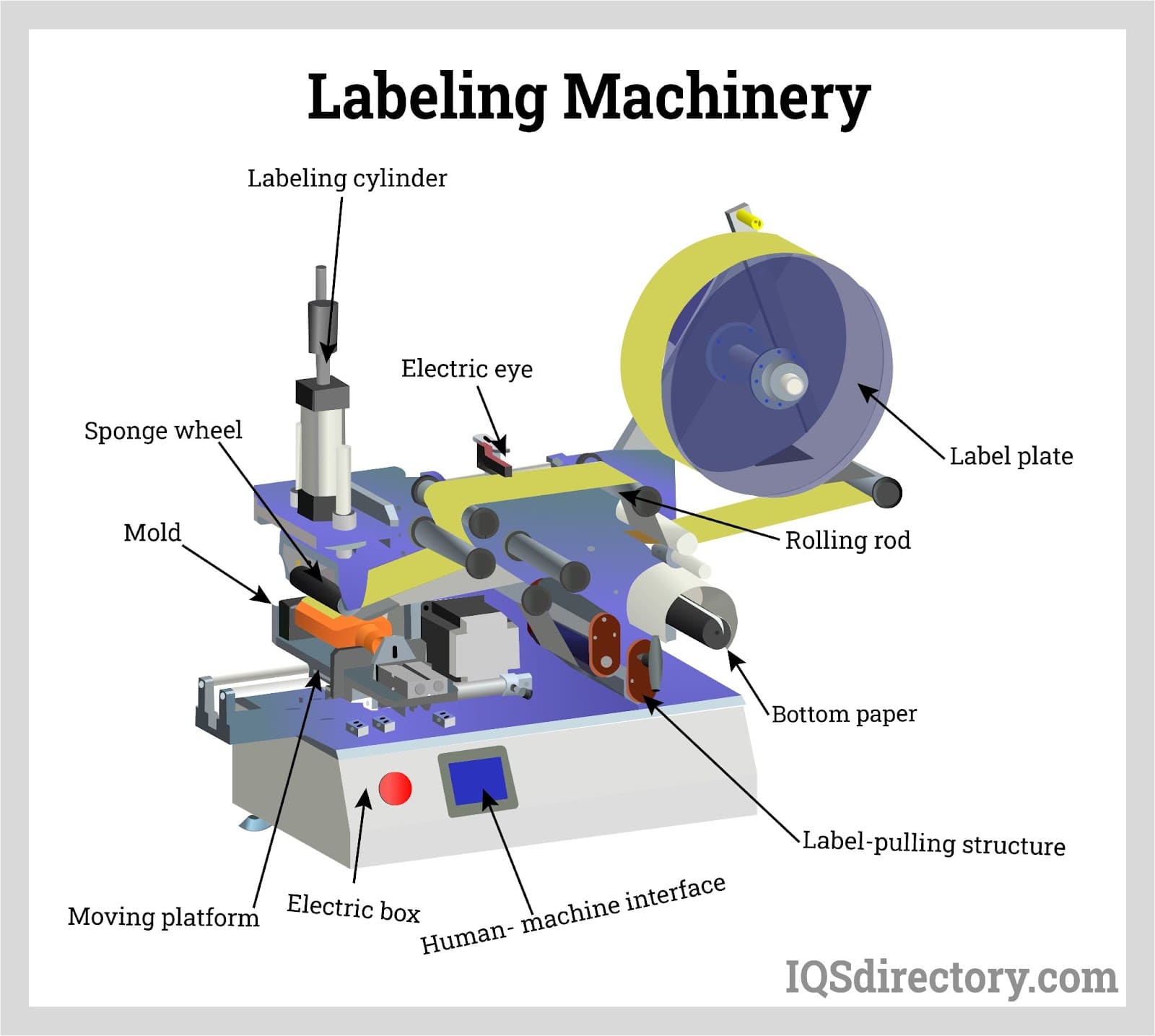
Hot Melt Adhesives: These thermoplastic adhesives are applied in a molten state and solidify rapidly, making them ideal for high-speed production lines in packaging, woodworking, and product assembly.
- Common use cases: Carton and box sealing, furniture assembly, bookbinding, filter manufacturing.
- Key benefits: Fast setting times, minimal waste, clean application with specialized equipment.
-
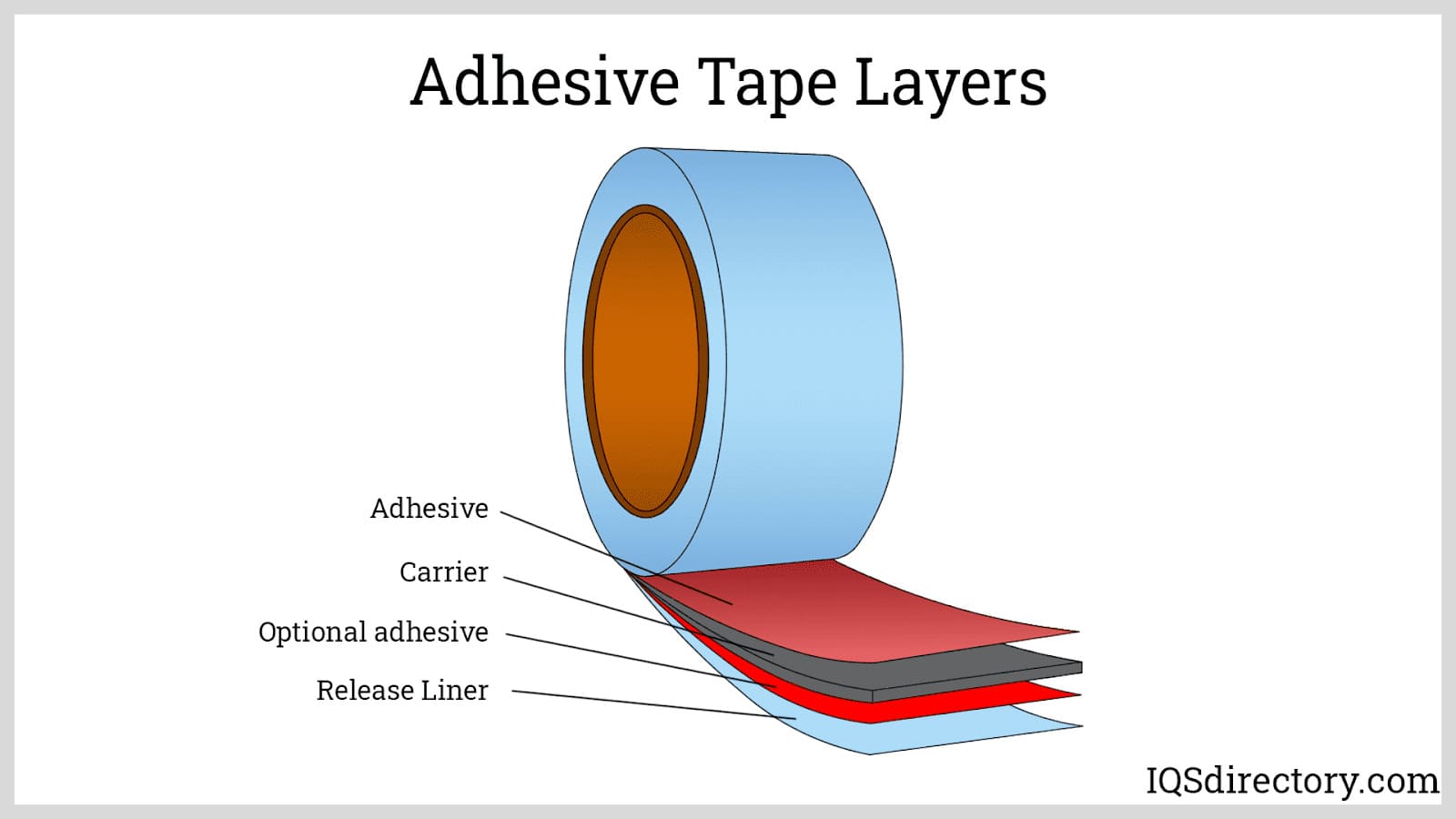
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs): Designed to form bonds when light pressure is applied, PSAs are crucial in labeling, tape manufacturing, and graphic applications.
- Common use cases: Labels, tapes, decals, protective films, signage.
- Key benefits: Immediate adhesion, removable or repositionable options, versatility across surfaces.
-
Acrylic Adhesives: Known for their UV resistance and weatherability, acrylics are common in signage, automotive trims, and construction where exposure to sunlight or harsh environments occurs.
- Common use cases: Outdoor signs, construction panels, vehicle trim assembly.
- Key benefits: Fast cure, high strength, excellent environmental resistance.
-
Silicone Adhesives: With superior temperature resistance and flexibility, silicone adhesives are widely used for electrical insulation, appliance manufacturing, and medical devices.
- Common use cases: Sealing joints, bonding glass or ceramics, gasketing in automotive and appliances.
- Key benefits: Flexible bonds, excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, electrical insulation properties.
Each adhesive type brings distinct advantages, ensuring there’s a solution tailored for nearly every industrial, commercial, or consumer application. For more information on how to choose the right adhesive type for your project, see our section below on “How to Select the Best Adhesive for Your Application.”
Limitations and Drawbacks of Adhesives
While adhesives offer a high degree of versatility, there are important limitations and potential drawbacks to consider when evaluating bonding solutions for your business or project:
- Removal and Rework: Many adhesives form permanent bonds, making disassembly, repair, or recycling challenging. Specialized solvents or mechanical force may be required to separate joined parts without damage.
- Temperature and Pressure Limitations: Some adhesives cannot withstand high-temperature or high-pressure environments. Selecting an adhesive that matches operational conditions is critical.
- Material Compatibility: Certain adhesives are not effective on porous, oily, or low-surface-energy materials like polyethylene or polypropylene. Surface preparation may be necessary to achieve optimal adhesion.
- Cure Time and Processing: Some adhesives require extended curing periods or specific environmental conditions (heat, humidity) to reach full strength, which may impact production timelines.
- Health and Safety: Many industrial adhesives contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other chemicals requiring ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE) during use.
Understanding these limitations can help you make informed decisions and select the right adhesive for your specific application needs. Not sure which adhesive is best for your environment? Contact our adhesive experts for tailored recommendations.
Benefits of Adhesives: Why Choose Adhesive Bonding?
Despite certain drawbacks, the advantages of adhesives drive their widespread adoption across industries. Here are the core benefits that position adhesives as a superior alternative to traditional fastening methods:
- Versatility: Adhesives can bond virtually any combination of substrates, including metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, composites, rubber, and wood. This enables innovative product designs and lightweight assemblies.
- Design Flexibility: Adhesives allow for invisible bonds and smooth surfaces, improving product aesthetics compared to screws, rivets, or welds.
- Stress Distribution: By spreading loads across bonded surfaces, adhesives reduce localized stresses and minimize the risk of material failure.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Adhesive assembly often streamlines production, reduces labor costs, and eliminates the need for drilling, tapping, or welding.
- Performance Enhancement: Many adhesives provide resistance to vibration, impact, chemicals, and moisture, improving product durability and performance.
- Lightweight Construction: Replacing mechanical fasteners with adhesives can reduce overall assembly weight, which is critical in aerospace, automotive, and electronics applications seeking improved energy efficiency.
- Sealing and Insulation: Adhesives can simultaneously bond and seal joints, providing electrical insulation, moisture barriers, or acoustic dampening as needed.
Compared to welding or soldering, adhesives offer faster assembly, cleaner aesthetics, and the ability to connect dissimilar materials. Their adaptability makes them an ideal solution for advanced manufacturing, rapid prototyping, industrial maintenance, and creative endeavors alike.
What are the Applications of Adhesives?
Are you wondering, “What industries use adhesives, and how do adhesives improve manufacturing processes?” The answer lies in their exceptional versatility. Adhesives are used as primary or supplemental bonding agents in virtually every sector, streamlining processes and enabling new product innovations. Here are some industry-specific applications and use cases:
Industrial Applications
- Automotive: Adhesives bond components such as panels, trim, glass, and structural elements, helping reduce vehicle weight (for better fuel efficiency) and improve crash resistance. Epoxies and polyurethanes are favored for their durability and vibration resistance.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, high-strength epoxy adhesives secure aircraft assemblies—composite panels, metal frames, interiors—where reliability under extreme conditions is paramount.
- Construction: Polyurethane and acrylic adhesives fasten flooring, roofing, insulation, and drywall, offering flexibility and moisture resistance. Silicone and hybrid sealants ensure airtight, weatherproof joints in building envelopes.
- Electronics: Cyanoacrylates and conductive adhesives are used in PCB assembly, component mounting, and sensor bonding, delivering precise, quick bonds without the thermal stress of soldering.
- Packaging: Hot melt adhesives seal boxes, cartons, and labels in high-speed production environments, prized for their rapid set and strong adhesion to paper, cardboard, and plastic films.
- Energy: Adhesives play a critical role in assembling solar panels, wind turbine blades, and battery packs, where lightweight, durable bonds optimize performance and longevity.
- Marine: Epoxies and polyurethanes are used to repair and assemble boats, resisting moisture, saltwater, and UV exposure.
Consumer and Commercial Applications
- Woodworking and Furniture: Cyanoacrylate and polyurethane adhesives bond wood joints, veneers, and laminates, accommodating natural expansion and contraction for long-lasting results.
- Medical and Healthcare: Medical-grade cyanoacrylates close wounds, bond surgical instruments, and secure prosthetics or dental restorations, offering biocompatibility and fast curing.
- Footwear and Textiles: Polyurethane adhesives are used to laminate fabrics and attach shoe soles, providing durability and flexibility under frequent wear.
- Arts, Crafts, and DIY: Hot melt, PVA, and other general-purpose adhesives make model building, crafting, and repair projects accessible and efficient for consumers.
- Signage and Displays: Pressure-sensitive and acrylic adhesives attach graphics, mount displays, and create weather-resistant signage for outdoor and retail applications.
Specialized and Emerging Applications
- Electromobility: Adhesives are crucial in electric vehicle (EV) battery assembly, providing thermal management, vibration resistance, and lightweight construction.
- Renewable Energy: Bonding and sealing in wind energy and solar panel installations ensures weatherproof, robust performance.
- Consumer Electronics: Adhesives play a role in smartphone and wearable device assembly, enabling miniaturized, durable designs.
- 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Specialty adhesives join printed components, enable hybrid assemblies, and support post-processing.
Advantages Driving Applications
Adhesives empower industries to:
- Bond dissimilar or hard-to-join materials (e.g., metal to plastic, composites to glass)
- Distribute mechanical stress evenly, reducing the risk of stress concentration and failure
- Accelerate assembly lines by enabling automation and rapid curing processes
- Improve aesthetics by eliminating unsightly mechanical fasteners
- Enhance product performance—resisting moisture, chemicals, vibration, and temperature extremes
Curious about which adhesive is best for your industry? Browse our comprehensive adhesives manufacturer listings or ask an expert for guidance on selecting the right bonding solution.
How to Select the Best Adhesive for Your Application
Choosing the ideal adhesive involves evaluating several critical factors to match your performance requirements, production processes, and regulatory needs. Consider the following when specifying an adhesive:
- Material Compatibility: Identify all materials to be bonded and consult manufacturer data sheets for recommended adhesive types.
- Strength and Durability: Assess mechanical loads, dynamic stresses, and long-term aging conditions.
- Environmental Conditions: Determine exposure to temperature swings, moisture, chemicals, or UV light.
- Processing Requirements: Consider cure time, application methods (manual, automated, spray, bead), and post-processing needs.
- Regulatory and Health Concerns: Ensure compliance with safety, environmental, or industry-specific standards (e.g., FDA, REACH, RoHS).
- Cost and Supply Chain: Balance performance benefits with unit price, availability, and supplier support.
Want to compare adhesive products or suppliers? Use our manufacturer directory to search by adhesive type, industry served, or location. Submit a Request for Quote (RFQ) to receive tailored offers and expert advice.
Choosing the Correct Adhesives Manufacturer: Decision Factors for Procurement
For businesses and procurement managers, selecting the right adhesives manufacturer or distributor is just as important as choosing the adhesive itself. Here’s how to approach your supplier search for optimal results:
- Expertise and Technical Support: Look for vendors with experience in your industry and the ability to provide formulation guidance, testing, and troubleshooting.
- Product Range and Customization: Evaluate manufacturers offering a broad portfolio of adhesive chemistries and custom solutions for unique applications.
- Certifications and Quality Assurance: Verify compliance with ISO, ASTM, or industry-specific quality standards.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Assess production capacity, lead times, and delivery logistics to ensure uninterrupted operations.
- Cost and Value: Compare pricing, minimum order quantities, and value-added services like private labeling or technical training.
To ensure a successful purchase of adhesives, compare at least five or six manufacturers using our curated list. Each supplier’s profile details their expertise and capabilities, and includes a contact form for inquiries or quotes. Use our website previewer to review each company’s specialization, then employ our RFQ form to contact multiple businesses with a single message.
Ready to streamline your adhesives sourcing process? Explore more adhesive manufacturers or request a quote today to find the perfect partner for your project.
Frequently Asked Questions About Adhesives
- What is the strongest adhesive for metal-to-metal bonding? Epoxy and acrylic adhesives are typically recommended for high-strength, structural metal bonding, offering excellent resistance to heat and chemicals.
- How do I remove cured adhesive from surfaces? Removal methods vary by adhesive type. Mechanical abrasion, heat, or specialized solvents may be required. Always consult manufacturer recommendations for safe and effective removal.
- Can adhesives replace welding or mechanical fasteners? In many applications, advanced adhesives can replace or supplement welding, rivets, or screws, providing lighter, more flexible assemblies. Consult an engineer to ensure compliance with structural requirements.
- Are there eco-friendly or low-VOC adhesives available? Yes, many manufacturers offer water-based, solvent-free, or bio-based adhesives with reduced environmental impact. Inquire about sustainable product lines when requesting quotes.
Optimize Your Adhesive Choices
Whether you’re developing new products, optimizing manufacturing processes, or tackling repair projects, the right adhesive can unlock superior performance and efficiency. Use our in-depth resources to:
- Research leading adhesive manufacturers for your application
- Compare epoxy, polyurethane, cyanoacrylate, hot melt, and specialty adhesive solutions
- Access expert advice on adhesive selection, application techniques, and troubleshooting
- Stay updated on the latest innovations in bonding technology
Still have questions? Contact us to discuss your project requirements and receive personalized product recommendations from our adhesive specialists.




 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services